Lean Manufacturing revolutionized the world with the systematic and documented approach to escalate the efficiency of any organizational value stream. Armed with many tools and techniques under its umbrella, Lean manufacturing offers a 360-degree evaluation framework for mitigating the non-value added activities from the system.
In order to understand the essence of it, we are aware that every “Process operation is a set of activities to produce a product or service“. So, every process has some value-added activities for which the customer pays, whereas most are non-value added.
These non-value-added activities are categories into the following two types:
- Necessary Waste
- Pure Waste
Necessary waste refers to activities that do not add any value to the product but support the value-added activities to some extent. But these activities should be minimized to save time and resources. Some of the examples are Law, Project coordination, quality, etc.
On the other hand, Pure Waste refers to activities that waste time and resources and should be removed from the process. There are seven deadly wastes (Muda) which are enlisted below:
- Over Production
- Defects
- Waiting
- Motion
- Over Processing
- Transporation
- Inventory
Among these seven, over-production is the disease for any process because it can cause other waste like inventory, waiting, etc.
Elimination of the non-value-added activities will indicate the success of any organization because it helps to improve the utilization of time and resources. In addition to this, there are four dimensions of performance illustrated in fig. 4 which are as follow:
- Cost/ Price
- Quality
- Flexibility
- Delivery
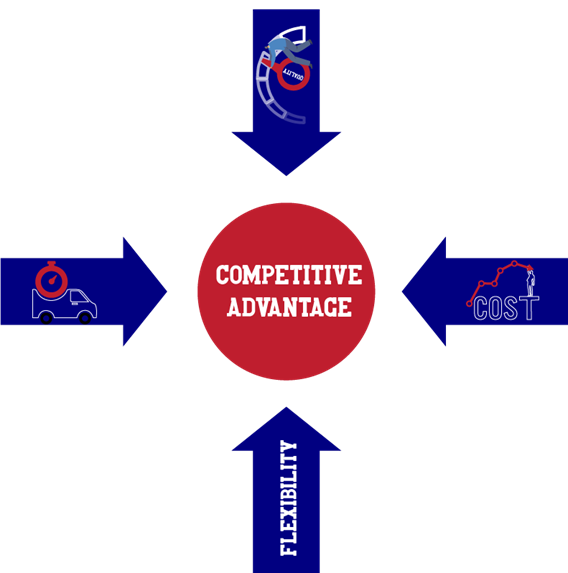
With the advent of technology and social media, the world has become a global village. Moreover, humankind are more conscious about the cost, quality, and delivery of the product or service
Fig 3 shows that quality, cost, and delivery time are the three parameters that define the success of any organization. Therefore, every organization tries to reduce its waste and improve quality, delivery time, and customer satisfaction. Lean is a concept without any boundaries, and the idea of Lean originated centuries ago, starting from the assembly lines of Henry Ford’s factories. But Toyota motors in Japan redefined the concept of Lean and became the market leader in no time.

Lean
“Lean is a way of creating needed value with lesser resources and less waste.”
It is a technique of production whose primary focus is to reduce waste and at the same time maintain productivity and customer satisfaction. Lean practices have strong roots in manufacturing industries and have produced remarkable results in the business management and service sector.
With the passage of time and the need of the industry, the concept of lean management is also reviving. Several practitioners have already contributed to improving lean management in the dynamics of the industry.
Goals of Lean manufacturing:
Some of the goals of the lean concept are given as follows.
- Elimination of waste: The foundation on which the lean concept was based is eliminating waste. This is the core idea on which the lean concept revolves around. The waste can be both material or immaterial. Besides physical wastes, examples of waste also include extra time or effort applied to perform any operation or task.
- Improve processes: Lean concept also works to improve the processes making them more effective, and this can be achieved by implementing poka-yoke or mistake-proofing.
- Improved product quality: By executing the lean concept, our goal is to manufacture improved quality products that can provide more value to the customers.
- Reduced cost: One of the critical and ultimate goal of lean concept that unnecassery costs should be decreased which consequently maximizes the revenue, making overall cost to the minimum.
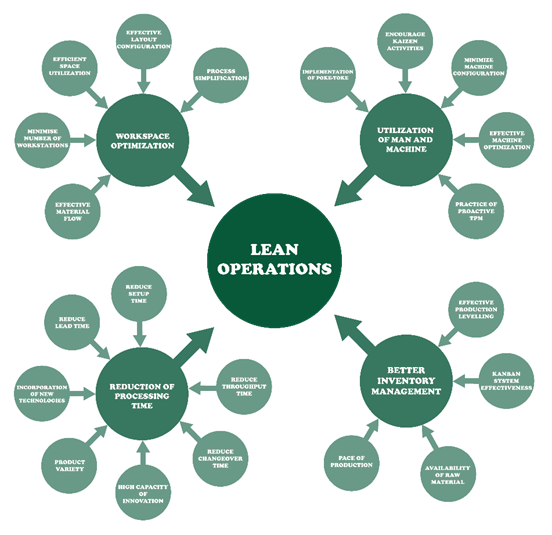
In fig. 4 shows the different lean operations which can facilitate the organization to effectively use their workspace buy effective inventory management and proper layout planning. Moreover, the organizations can improve productivity by effectively utilizing resources like man and machine, which also helps to reduce the processing and lead time.
Moreover, it impacts the way of working of an organization and helps achieve the goals and targets. Its impact on organizations can be determined by the success stories of businesses that have excelled so much in their respective fields by implementing lean strategy.
